Overtime Pay BC
In today’s competitive work environment, overtime pay is a crucial aspect of fair compensation for employees who exceed standard working hours. If you’re employed in British Columbia (BC), it’s essential to know your rights regarding overtime pay under the British Columbia Employment Standards Act (ESA). This guide will walk you through everything you need to understand about OT and how to make claims under BC law.
What is Overtime Pay?
Overtime pay refers to the additional compensation employees receive for hours worked beyond the standard workweek or workday.
Daily Overtime Pay BC: In British Columbia, the standard workday is typically 8 hours with employees qualifying for overtime pay when they work beyond this threshold unless exempted under specific circumstances outlined in the ESA. Employees receive time-and-a-half for hours worked beyond 8 in a day, up to 12 hours, regardless of whether or not they work over 40 hours weekly. Beyond 12 hours in a day, employees receive double-time pay.
Weekly Overtime Pay BC: The standard workweek is typically 40 hours, and any hours worked beyond this threshold qualify for overtime pay, unless exempted under specific circumstances outlined in the ESA.
Employees earn time-and-a-half for hours worked beyond 40 total hours in a week, regardless of how many daily hours they work (i.e. even if they do not work more than 8 hours on any given day). The workweek spans Sunday to Saturday, with only the initial 8 daily hours contributing to weekly overtime calculations (so as to avoid receiving both weekly OT and daily OT for the same hours).
Workers are also entitled to overtime pay if employers do not provide them with adequate rest periods: Employers are required to provide employees with either a continuous 32-hour break from work each week or compensate them at 1 1/2 times their regular wage for any time worked during the break period. Additionally, employers must ensure that employees have a minimum of 8 consecutive hours off between each shift worked.
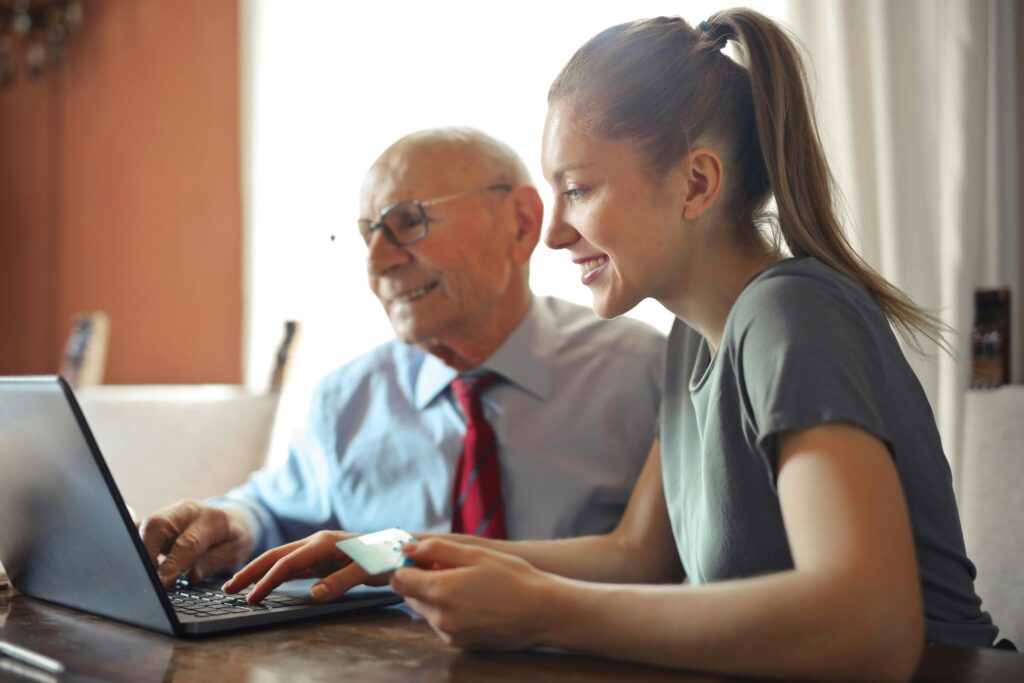

Key Points to Know About Overtime Pay BC
• Eligibility: Most employees in BC are entitled to overtime pay unless they fall under specific exemptions such as managerial or supervisory roles.
• Rate of Pay: Employees are generally entitled to overtime pay at a rate of at least 1.5 times their regular hourly wage for each hour of overtime worked.
• Overtime Threshold: Overtime pay applies after an employee exceeds 8 hours of work in a day or 40 hours in a week.
• Calculating Overtime: Overtime hours are calculated based on a single workweek (for both daily OT and weekly OT).
Example: If you work 10 hours a day for six days, you would be entitled to 2 hours of daily OT for each 10 hour workday for a total of 12 daily OT hours for the workweek. For weekly OT, only the initial 8 hours in any given workday are counted. In this example, that would mean 48 hours are counted for weekly OT purposes, meaning that, in addition to 12 hours of daily OT, you would be entitled to 8 hours of weekly OT.
In British Columbia, most employees are entitled to overtime pay under the ESA, whether they are salaried or paid hourly. There are, however, certain professions are exempt from these overtime rules.
For employees in these exempt categories, different overtime rules may apply, but in general, managers, professionals, and high-tech workers are not entitled to OT pay. Note that to qualify as a “manager,” you must have actual supervisory authority over other employees’ work, not simply hold the managerial title.
Under the ESA, the following categories of workers are not entitled to OT:
- Managers
- Transportation industry workers
- Oil and gas industry workers
- Forestry workers
- High-tech workers
- Farm workers
- Most professionals
For most other employees, regardless of their salary or hourly wage, overtime pay applies. For more detailed information (including the full list of jobs exempt from OT), refer to the Employment Standards Regulations, BC Reg 396/95 part 7 (click here to view part 7 of the regulations).
Banking Overtime Pay
Employees can choose to bank their overtime by making a written request to save the hours instead of being paid for them immediately. Later, they can:
1. Request part or all of the banked wages to be paid out;
2. Take paid time off, as agreed with the employer; or
3. Ask the employer to close the time bank and pay out all banked hours (in writing).
An employer can also close a time bank with one month’s written notice and must, within six months:
1. Pay out all banked overtime wages;
2. Allow the employee to take paid time off using the banked hours; or
3. Partially pay out the banked wages and allow the rest to be used for paid time off.
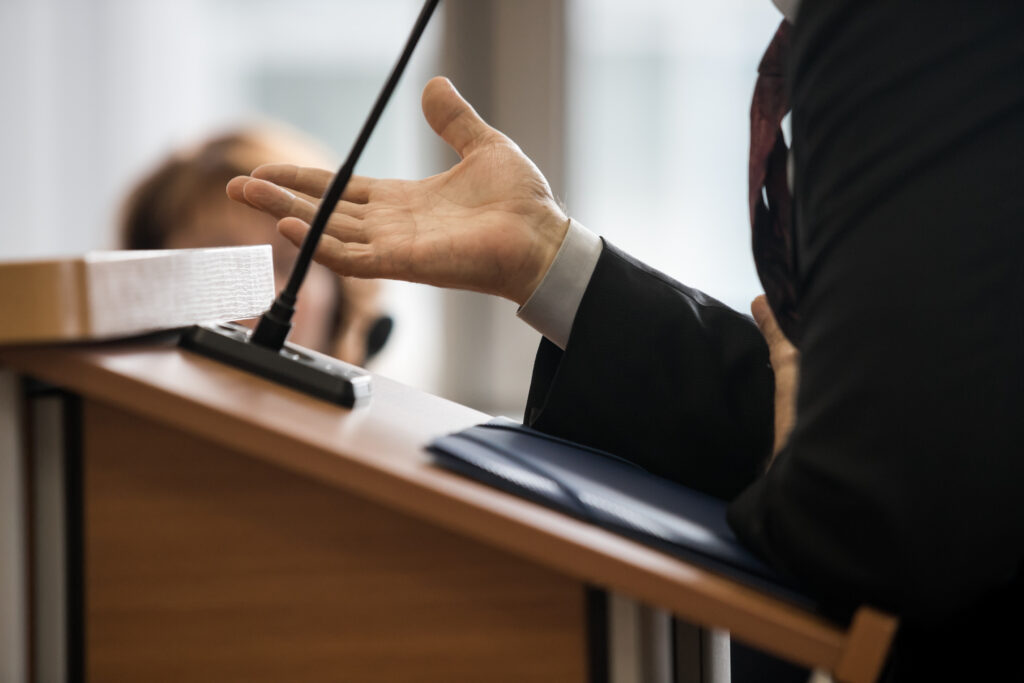

Making Overtime Pay Claims: Step-by-Step
If you believe you’re entitled to overtime pay and haven’t received it, here’s what you should do:
1. Document Your Hours: Keep detailed records of your work hours, including start times, end times, and any breaks taken.
2. Review Your Employment Contract: Check if your employment contract outlines specific terms related to overtime pay. However, remember that the ESA sets minimum standards, which cannot be waived or reduced by contract.
3. Initiate a Discussion: Start by discussing the issue with your employer. Often, misunderstandings or errors in payroll processing can be resolved amicably at this stage.
4. File a Complaint: If discussions with your employer do not resolve the issue, you can file a formal complaint with the Employment Standards Branch of BC. Provide them with your documented evidence of hours worked and details of your attempts to resolve the matter with your employer.
5. Seek Legal Advice: If your employer refuses to comply with ESA standards or if you encounter any complications during the complaint process, seeking legal advice from an employment lawyer specializing in BC employment law can be beneficial. They can provide guidance tailored to your situation and ensure your rights are protected.
Understanding your rights regarding overtime pay in British Columbia is crucial to ensuring fair compensation for your hard work. By familiarizing yourself with the ESA guidelines and taking proactive steps when necessary, you can navigate overtime pay issues effectively. Remember, timely documentation and seeking advice from legal professionals when needed can significantly strengthen your position when making overtime claims.
For more detailed information or assistance with overtime pay claims in British Columbia, contact Bay View Law, your trusted employment law firm dedicated to protecting workers’ rights across BC. Our experience covers negotiated OT settlements, contractual OT claims, and assisting employees with OT complaints through the Employment Standards Branch of BC.
If you found this information helpful, see our introduction to severance here.
